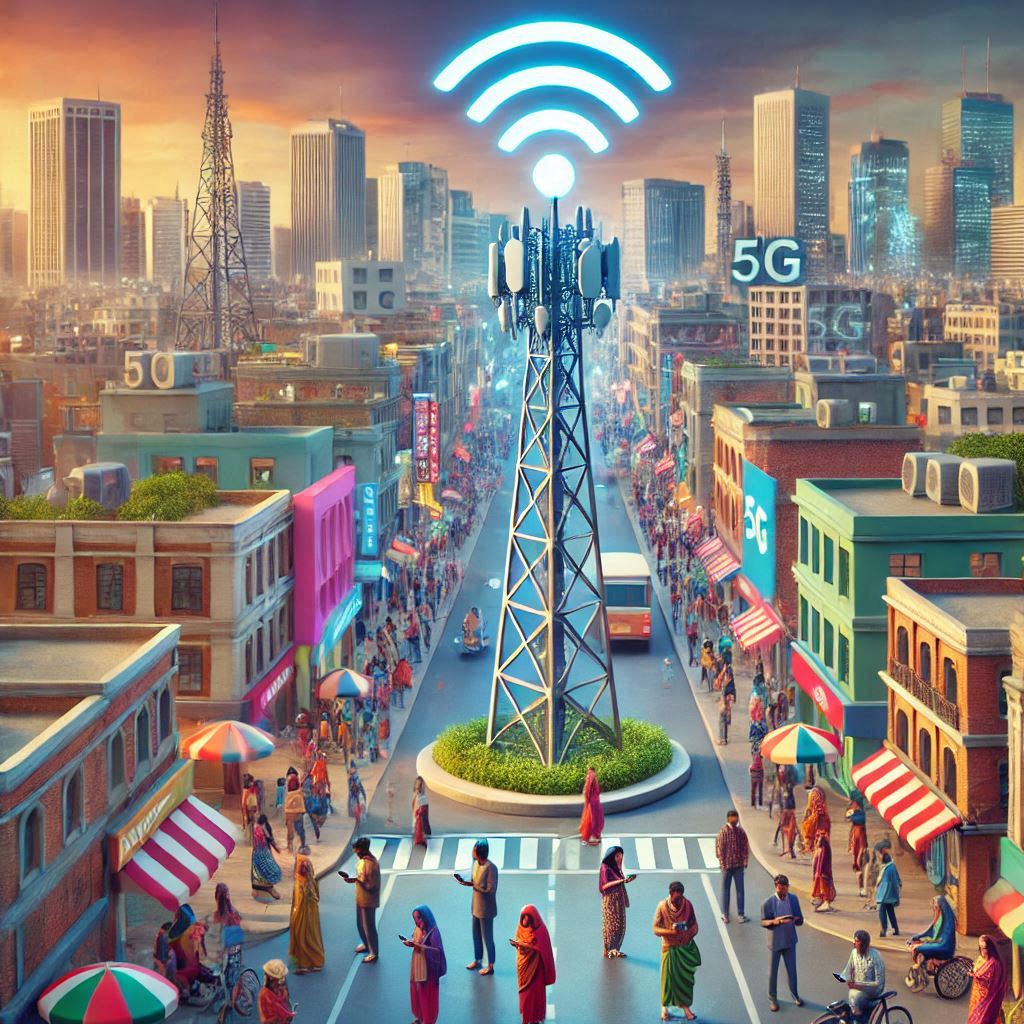
The fifth-generation (5G) network is more than just an upgrade from its predecessor—it’s a technological revolution that promises to transform industries, economies, and societies. As nations worldwide embrace this advanced connectivity, Bangladesh has also joined the race to adopt 5G, with aspirations of accelerating digital transformation and fostering economic growth. This article explores the status, potential, and challenges of 5G deployment in Bangladesh, providing a comprehensive overview of its implications for the country.
What is 5G?
5G is the latest generation of mobile network technology, offering significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to 4G. Its key features include:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Provides ultra-fast internet speeds, enabling seamless streaming, downloading, and real-time interaction.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): Supports large-scale Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity for smart cities, agriculture, and industries.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC): Enables real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation.
These features position 5G as a foundational technology for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0), driving innovation and economic opportunities.
The State of 5G in Bangladesh.
Bangladesh officially launched its first 5G services in December 2021, becoming one of the early adopters in South Asia. The launch was spearheaded by state-owned mobile operator Teletalk, with limited coverage in select areas, including parts of Dhaka and nearby regions. Since then, other telecom operators, such as Grameenphone, Robi, and Banglalink, have expressed their commitment to rolling out 5G networks in the near future.
The government has identified 5G as a strategic priority under its “Vision 2041” plan, aiming to transform Bangladesh into a developed nation by leveraging digital technologies. Key milestones include:
Spectrum Auction: In 2022, Bangladesh Telecommunications Regulatory Commission (BTRC) held spectrum auctions to allocate the necessary frequencies for 5G deployment.
Infrastructure Development: Telecom operators are investing in upgrading their existing infrastructure to support 5G technology.
Pilot Projects: Several pilot projects have been launched to test 5G capabilities in industrial, healthcare, and urban environments.
The Potential of 5G in Bangladesh.
The adoption of 5G has far-reaching implications for Bangladesh’s economy and society. Some of the key areas where 5G can make a significant impact include:
- Economic Growth.
5G is expected to act as a catalyst for economic development by:
Boosting Productivity: Faster and more reliable connectivity enables businesses to adopt automation and advanced analytics, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Attracting Investment: The availability of 5G infrastructure makes Bangladesh more attractive to foreign investors in technology, manufacturing, and services.
Job Creation: The 5G ecosystem creates opportunities in telecommunications, IT, and related industries, fostering job growth.
- Smart Cities.
5G can revolutionize urban management and improve the quality of life through smart city applications such as:
Traffic Management: IoT-enabled sensors and real-time data analysis can reduce congestion and improve transportation efficiency.
Energy Optimization: Smart grids and connected devices can monitor and optimize energy usage, reducing waste.
Public Safety: High-speed communication supports advanced surveillance systems and emergency response mechanisms.
- Healthcare.
The healthcare sector in Bangladesh can benefit immensely from 5G-enabled innovations such as:
Telemedicine: High-speed, low-latency networks enable real-time consultations and remote monitoring, improving access to healthcare in rural areas.
Remote Surgery: Surgeons can perform operations from a distance using robotic systems connected via 5G.
Data Management: Connected devices can collect and analyze patient data for better diagnosis and treatment.
- Agriculture.
As an agriculture-dependent country, Bangladesh can leverage 5G for smart farming solutions, including:
Precision Agriculture: Sensors and drones can monitor soil health, crop conditions, and weather patterns to optimize farming practices.
Supply Chain Management: IoT-enabled systems can improve the efficiency of agricultural supply chains, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
Farmer Connectivity: Rural farmers can access market information, weather updates, and agricultural advice through mobile applications.
- Education.
5G can transform education in Bangladesh by:
Enabling Remote Learning: High-speed connectivity supports interactive online classes and virtual labs.
Access to Resources: Students can access a wealth of educational content and collaborate with peers and teachers globally.
Skill Development: 5G-powered technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) provide hands-on learning experiences.
- Industry and Manufacturing.
The manufacturing sector can adopt 5G for:
Industrial Automation: Real-time monitoring and control of machines improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Supply Chain Visibility: IoT devices track goods throughout the production and delivery process, enhancing transparency.
Robotics: 5G enables the use of autonomous robots for tasks like assembly, inspection, and packaging.
Challenges to 5G Implementation.
While the prospects of 5G in Bangladesh are promising, several challenges must be addressed to ensure successful deployment and adoption:
- High Costs.
The cost of deploying 5G infrastructure, including spectrum acquisition, network upgrades, and equipment procurement, is substantial. Telecom operators need significant investments, and affordability may become an issue for consumers.
- Infrastructure Limitations.
Bangladesh’s existing telecom infrastructure requires extensive upgrades to support 5G. The lack of fiber-optic networks, especially in rural areas, poses a major obstacle.
- Regulatory Hurdles.
Ensuring a smooth rollout of 5G requires clear and supportive policies from regulators. Delays in spectrum allocation or licensing can hinder progress.
- Digital Divide.
The disparity in internet access between urban and rural areas may widen with 5G deployment. Ensuring equitable access is crucial to avoid excluding underserved communities.
- Skilled Workforce.
A shortage of skilled professionals in telecommunications and IT may slow down the adoption and maintenance of 5G networks.
- Cybersecurity Concerns.
The increased connectivity brought by 5G also heightens the risk of cyber threats. Robust security measures are essential to protect networks and user data.
Government and Private Sector Initiatives.
The Bangladeshi government and private sector are actively working to overcome these challenges and accelerate 5G deployment. Key initiatives include:
Policy Support: The government has introduced incentives for telecom operators to invest in 5G infrastructure and is revising regulatory frameworks to facilitate its rollout.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between government agencies and private companies are driving investment and innovation in the 5G ecosystem.
Capacity Building: Training programs and educational initiatives are being launched to develop a skilled workforce for 5G-related jobs.
Pilot Projects: Demonstration projects in smart cities, agriculture, and healthcare are showcasing the potential of 5G and encouraging adoption.
The Global Context.
Bangladesh’s efforts to adopt 5G align with global trends, as countries worldwide embrace this transformative technology. Leading nations such as the United States, China, South Korea, and Germany are leveraging 5G to drive economic growth and technological innovation. By learning from the experiences of these countries, Bangladesh can avoid pitfalls and adopt best practices to maximize the benefits of 5G.
The Road Ahead.
The successful implementation of 5G in Bangladesh will require a coordinated effort from all stakeholders, including the government, telecom operators, technology providers, and consumers. Key priorities for the future include:
Expanding Infrastructure: Accelerating the rollout of fiber-optic networks and base stations to ensure nationwide coverage.
Affordable Access: Developing pricing models and subsidies to make 5G services affordable for all citizens.
Promoting Innovation: Supporting startups and research initiatives that leverage 5G for new applications and solutions.
Strengthening Security: Implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks to safeguard networks and users.
Public Awareness: Educating consumers about the benefits of 5G and addressing misconceptions.
Conclusion.
The 5G network represents a transformative opportunity for Bangladesh, offering the potential to accelerate digital transformation, boost economic growth, and improve quality of life. While challenges remain, the commitment of the government, private sector, and society as a whole ensures that 5G can play a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s future. By embracing this cutting-edge technology, Bangladesh can position itself as a leader in the digital age and unlock new horizons of innovation and progress.